Matching principles for high pressure hoses and crimpers
 2024.11.01
2024.11.01
 Industry News
Industry News
Cheap and high quality high pressure hose crimper supply
In industrial production and daily maintenance, high pressure hoses are widely used due to their high pressure resistance, corrosion resistance, and flexibility. However, to ensure the safety and reliability of high pressure hoses, it is crucial to correctly choose and use a high pressure hose crimper. This article analyzes the requirements of different materials and specifications of high pressure hoses for crimpers and provides a guide to selecting the right crimping tool.
Types and Characteristics of High Pressure Hoses
High pressure hoses can be classified by material into rubber hoses, polyurethane hoses, PVC hoses, and metal-braided hoses. Each type has unique characteristics and applications:
Rubber Hoses: Known for their good oil and wear resistance, they are suitable for hydraulic systems and the petroleum industry.
Polyurethane Hoses: Resistant to low temperatures and chemical corrosion, they are ideal for the food and pharmaceutical industries.
PVC Hoses: Lightweight and transparent, they are commonly used for water and air transfer.
Metal-Braided Hoses: Highly resistant to high temperatures and pressures, they are widely used in chemical and aerospace industries.
Specifications of High Pressure Hoses
The specifications of high pressure hoses typically include inner diameter, outer diameter, wall thickness, and length. These parameters directly affect the hose's pressure resistance and application:
Inner Diameter: Determines the flow rate and velocity of the fluid. Choose based on the system's flow requirements.
Outer Diameter: Influences the installation space and bending radius. Ensure it matches the connecting components.
Wall Thickness: Relates to the hose's pressure resistance; thicker walls mean higher pressure resistance.
Length: Select based on actual application needs. Too long can increase resistance, while too short can limit movement.
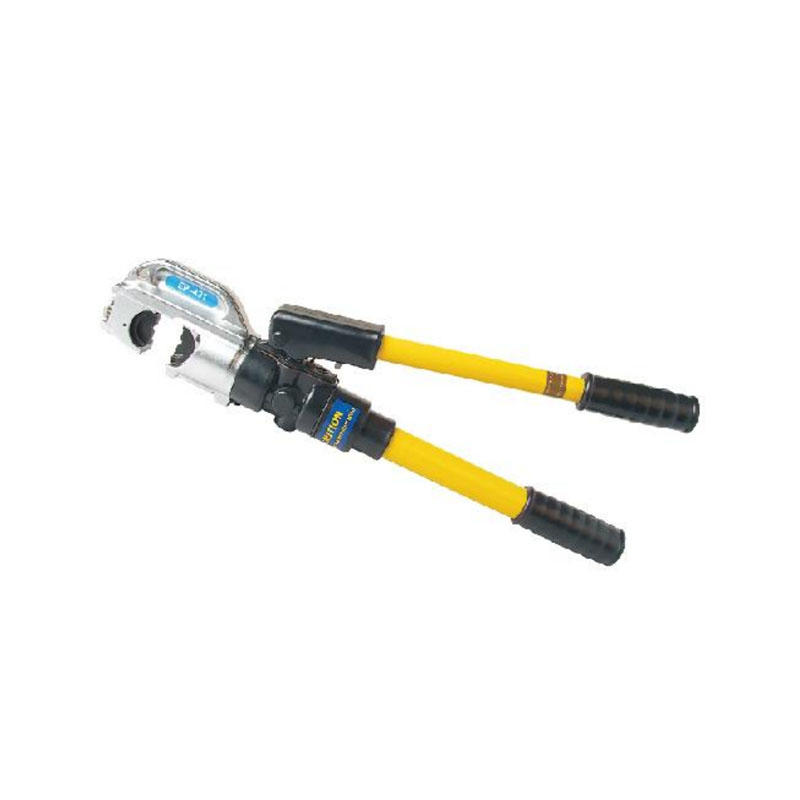
Selection Principles for High Pressure Hose Crimpers
Material Compatibility: Different materials require different crimping methods and tools. For example, rubber hoses typically use mechanical crimpers, while metal-braided hoses require hydraulic high pressure hose crimpers.
Specification Adaptability: The high pressure hose crimper should accommodate various hose sizes. Choose a crimper with a wide crimping range to cover your needs.
Crimping Force: This is a critical performance metric. The wall thickness and material of the hose determine the required crimping force. Ensure the crimper can meet the hose's pressure requirements.
Ease of Operation: An efficient crimper should have a simple operation process and clear indicators to minimize errors and improve efficiency.
Durability: A high-quality high pressure hose crimper should be durable and stable, capable of long-term use in harsh environments.
Safety: Safety is paramount. The crimper should have robust safety features such as overload protection and emergency stop buttons to ensure operator safety.
Steps for Crimping High Pressure Hoses
Preparation: Ensure the high pressure hose and fitting are clean and free of debris. Check the high pressure hose crimper for any issues and connect the power or air source.
Install the Fitting: Insert the fitting into the end of the high pressure hose, ensuring it is fully seated.
Position for Crimping: Place the hose with the fitting into the crimper's die, adjusting the position so the fitting is centered.
Start Crimping: Activate the high pressure hose crimper and follow the device's instructions for crimping. Keep the process steady and avoid sudden movements or interruptions.
Check the Crimp: After crimping, inspect the connection between the fitting and the hose to ensure it is secure and leak-free. Perform a pressure test if necessary to verify the crimp quality.
Common Issues and Solutions
Loose Crimp: This may be due to insufficient crimping force or an incorrect die. Adjust the crimping force or replace the die.
Fitting Dislodgement: Check if the fitting and hose are clean and if the fitting is fully inserted. Re-crimp if necessary.
Crimper Malfunction: Regularly maintain the high pressure hose crimper, checking the hydraulic oil level, filters, and seals to ensure proper operation.
Operational Errors: Provide adequate training to operators to ensure they are familiar with the operation procedures and safety guidelines.
Conclusion
Correctly choosing and using a high pressure hose crimper is essential for ensuring the quality and safety of high pressure hose connections. By understanding the requirements of different materials and specifications of high pressure hoses, you can select the appropriate crimping tool, enhancing efficiency and extending the service life of the equipment. This guide aims to help you make informed decisions and ensure reliable operation of high pressure hose systems.



 Español
Español русский
русский